There are no products for this injury yet.
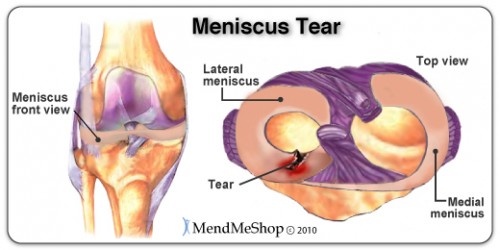
Meniscuses play a key role in joint shock absorbing, but their poor blood circulation causes weak healing opportunities. The injures are divided into elongated, radial and compound. Medial meniscal injury is the most common. Patomechanism is based on sudden extend of bended and rotated knee or on hyperextension. Twisting motions, occur in sports such as American football, basketball or football (soccer), cause huge risk to meniscal tearing in it. In extreme cases, the injury leads to inability to fully knee extension (it’s called ‘locked knee’).
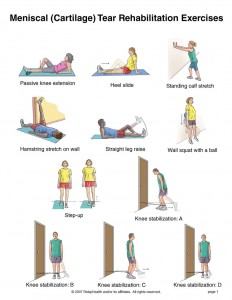
Exercises
1) Passive knee extension:
– lie on your back and put a rolled-up towel under the heel of your injured leg
– relax your muscles and let gravity to extend your knee
– hold this position for 2-5 minutes
– repeat exercise 5 times a day
2) Heel slide:
– sit on the floor with straighten legs
– gently slide the heel of your injured leg on the floor with pulling knee toward your chest
– return slowly
– do 10 sets
3) Hamstring stretch on the wall:
– lie on your back with your buttocks close to a doorway
– raise your injured leg and rest on the wall as high and straight as you can to feel a stretch in the back of your thigh
– hold position for 20 seconds and relax
– practice exercise 10 times
4) Straight leg raise:
– lie on your back and support yourself on your forearms
– bend your injured leg in knee joint
– raise your shin to make the leg straighten
– hold it for 5 seconds and return slowly
– practice exercise 15 times
5) Wall squat with a ball:
– stand straight your back to the wall with the soft ball between the wall and the back
– slowly squat down to keep your thighs not parallel to the floor
– hold it for 10 seconds and return slowly
– practice exercise 10 times
6) Step-up exercise:
– stand on the injured leg on a support (with gently bending your knee and hip) to put the other leg (foot) on the floor
– extend your hip and knee of the injured leg to the other leg comes off the floor
– hold position for 5 second and return slowly
– practice exercise 15 times
7) Resisted knee flexion:
– stand your face to the door
– tie a knot on the end of elastic tubing and put it around the ankle on your injured side
– tie a knot on the second end of the tubing and put it around the door
– extend your leg to the back keeping its straight and get back slowly
– practice exercise 15 times
8) Resisted hip abduction:
– stand your uninjured side to the door
– tie a knot on the end of elastic tubing and put it around the ankle on your injured side
– tie a knot on the second end of the tubing and put it around the door
– move your injured leg out to the side keeping its straight and return slowly
– practice exercise 15 times
9) Resisted knee extension:
– stand your back to the door
– tie a knot in one end of the tubing around the ankle of your injured leg
– tie a knot in other end of the tubing around the door
– extend your knee and return slowly
– repeat exercise 15 times
10) Resisted hip adduction:
– stand your injured side to the door
– tie a knot on the end of elastic tubing and put it around the ankle on your injured side
– tie a knot on the second end of the tubing and put it around the door
– move your injured leg away the door keeping its straight and return slowly
– practice exercise 15 times